

|
Ammonia emerges as most feasible alternative fuel for deep-sea shipping in 2050 emissions study
Research combining expert survey and technical analysis ranks ammonia ahead of hydrogen and methanol. |
|
|
|
||

|
EMSA study examines biodiesel blend spill response as shipping adopts alternative fuels
Research addresses knowledge gaps on biodiesel-conventional fuel blends as marine pollutants and response measures. |
|
|
|
||

|
BIMCO adopts ETS clause for bareboat charters, delays biofuel provision
BIMCO’s Documentary Committee has approved an emissions trading compliance clause while requesting further work on a biofuel charter provision. |
|
|
|
||

|
BIMCO and Norwegian Shipbrokers’ Association launch SALEFORM 2025 ship sale contract
Updated agreement addresses banking changes, compliance requirements and environmental regulations affecting vessel transactions. |
|
|
|
||
|
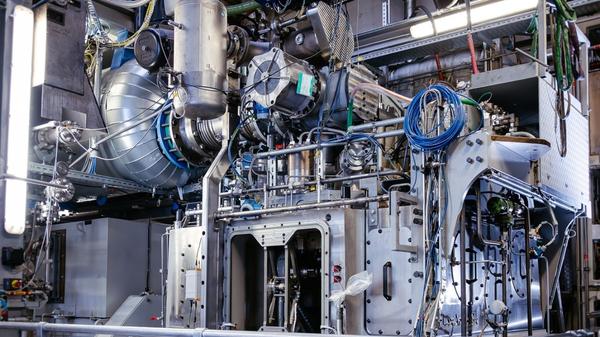
Everllence develops hydrogen test bench for marine engines
German engine maker upgrades Augsburg facility under HydroPoLEn project backed by federal maritime research funding. |
|
|
|
||

|
CMA CGM names 13,000-teu methanol-fuelled containership in South Korea
CMA CGM Osmium to operate on Asia–Mexico service as part of the carrier’s decarbonisation strategy. |
|
|
|
||

|
NorthStandard publishes biofuel guide as marine insurance claims emerge
White paper addresses quality issues and compliance requirements as biofuel testing volumes surge twelvefold. |
|
|
|
||

|
Maritime fuel platform calls for EU shipping ETS revenues to fund clean fuel deployment
Clean Maritime Fuels Platform urges earmarking of national emissions trading revenues for renewable fuel infrastructure. |
|
|
|
||

|
Lloyd’s Register grants approval for hybrid nuclear power design for amphibious vessels
Classification society approves Seatransport’s concept integrating micro modular reactors with diesel-electric systems. |
|
|
|
||
|
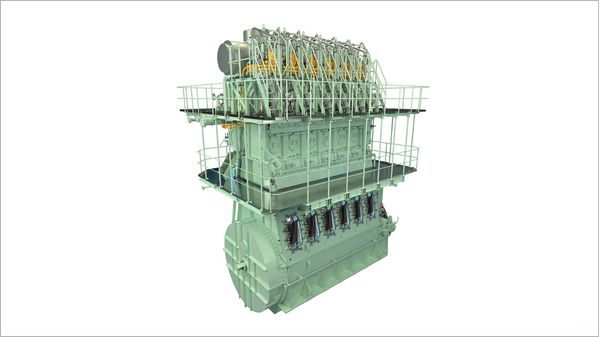
Everllence and Vale partner on ethanol-powered marine engine development
Brazilian mining company to develop dual-fuel ethanol engines based on ME-LGI platform. |
|
|
|
||
| Shipping confidence falls to new low [News & Insights] |
| Rising fuel costs hit shipping confidence [News & Insights] |
| Shell to launch lubricant in 2012 [News & Insights] |
| 50-year supply partnership for oil major [News & Insights] |