

|
Lloyd’s Register grants approval for hybrid nuclear power design for amphibious vessels
Classification society approves Seatransport’s concept integrating micro modular reactors with diesel-electric systems. |
|
|
|
||
|
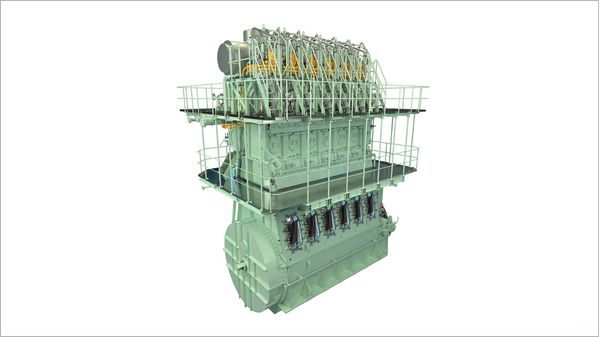
Everllence and Vale partner on ethanol-powered marine engine development
Brazilian mining company to develop dual-fuel ethanol engines based on ME-LGI platform. |
|
|
|
||

|
Emvolon highlights biomethanol as a solution to unlock India’s biogas potential
Company says distributed biogas-to-biomethanol production could bridge rural feedstock with maritime fuel demand. |
|
|
|
||

|
Grimaldi's Grande Svezia makes inaugural Le Havre call with ammonia-ready design
Second of 10 new-generation PCTCs features 5 MWh battery system and cold ironing capability. |
|
|
|
||

|
Kongsberg Maritime to supply integrated systems for LS Marine Solution cable lay vessel
Norwegian technology provider wins contract for ultra-large vessel being built at Tersan Shipyard in Türkiye. |
|
|
|
||

|
Synergy Marine takes on management of methanol dual-fuel container vessel
The 5,915-teu Maersk Finisterre joins Synergy's fleet under technical management from Synergy Pacific. |
|
|
|
||

|
Verde Marine Energy appoints Steve Taylor as UK director
Taylor will be based on the River Humber, working with Vertom Group businesses. |
|
|
|
||

|
Mitsubishi Shipbuilding delivers first ammonia fuel supply systems for marine engines
Systems shipped to Japan Engine Corporation for integration with an ammonia-fuelled marine engine. |
|
|
|
||

|
Power2X acquires HyCC to expand green hydrogen portfolio in the Netherlands and Germany
Deal consolidates clean molecules sector as projects transition from development to large-scale delivery phase. |
|
|
|
||

|
RFOcean signs binding e-methanol supply deal with ETFuels from 2030
European shipping company secures fixed-price green fuel ahead of escalating EU maritime emissions penalties. |
|
|
|
||
| Indian firm coats ship in bid to reduce bunker costs [News & Insights] |
| German firm supplies fuel savings system [News & Insights] |
| Low emission tug wins Clean Air Technology Award [News & Insights] |