
|
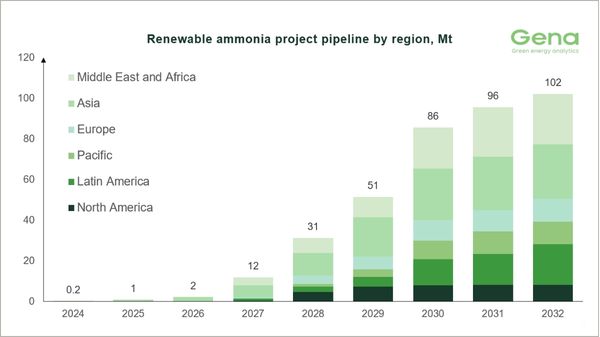
Clean ammonia project pipeline shrinks as offtake agreements remain scarce
Renewable ammonia pipeline falls 0.9 Mt while only 3% of projects secure binding supply deals. |
|
|
|
||

|
Thoen Bio Energy joins Global Ethanol Association
Shipping group with Brazilian ethanol ties becomes member as association plans export-focused project group. |
|
|
|
||

|
Norway enforces zero-emission rules for cruise ships in World Heritage fjords
Passenger vessels under 10,000 GT must use zero-emission fuels in Geirangerfjord and Nærøyfjord from January 2026. |
|
|
|
||

|
Longitude unveils compact PSV design targeting cost efficiency
Design consultancy launches D-Flex vessel as a cost-efficient alternative to larger platform supply vessels. |
|
|
|
||

|
IBIA seeks advisor for technical, regulatory and training role
Remote position will support the association’s IMO and EU engagement and member training activities. |
|
|
|
||

|
Barents NaturGass begins LNG bunkering operations for Havila Kystruten in Hammerfest
Norwegian supplier completes first truck-to-ship operation using newly approved two-truck simultaneous bunkering design. |
|
|
|
||
|
Everllence receives 2,000th dual-fuel engine order from Cosco
Chinese shipping line orders 12 methane-fuelled engines for new 18,000-teu container vessels. |
|
|
|
||

|
NYK signs long-term charter deals with Cheniere for new LNG carriers
Japanese shipping company partners with Ocean Yield for vessels to be delivered from 2028. |
|
|
|
||

|
Sallaum Lines takes delivery of LNG-powered container vessel MV Ocean Legacy
Shipping company receives new dual-fuel vessel from Chinese shipyard as part of fleet modernisation programme. |
|
|
|
||

|
Rotterdam bio-LNG bunkering surges sixfold as alternative marine fuels gain traction
Port handled 17,644 cbm of bio-LNG in 2025, while biomethanol volumes tripled year-on-year. |
|
|
|
||
| Unifeeder to implement SECA surcharge to cover higher fuel costs [News & Insights] |
| Surcharge heads-up: Bunker costs will 'substantially increase', says shipper [News & Insights] |
| Stena Line to raise freight prices due to SECA fuel switch rules [News & Insights] |
| MSC announces ECA charges [News & Insights] |
| Horizon's bunker costs down $23 per tonne in Q2 [News & Insights] |